| LIBROW | ® |
| Products | Solutions | Vehicles | Articles | Inquiry | Contacts | My account |
Article 11 — Appendix A.6
arcsch — arc-hyperbolic cosecant function
Category. Mathematics.
Abstract. Arc-hyperbolic cosecant: definition, plot, properties and identities.
Reference. This article is a part of Librow scientific formula calculator project.
Limited offer
Professional Librow Calculatorvisit
for free
- Bessel functions
- gamma function
- complex numbers
7.4 MB for Windows
1. Definition
Arc-hyperbolic cosecant is inverse of hyperbolic cosecant function. With the help of natural logarithm it can be represented as:
arcschx ≡ ln[1/x + √(1/x2 + 1)]2. Plot
Arc-hyperbolic cosecant is antisymmetric function defined everywhere on real axis, except its singular point 0 — so, its domain is (−∞, 0)∪(0, +∞). Function plot is depicted below — fig. 1.
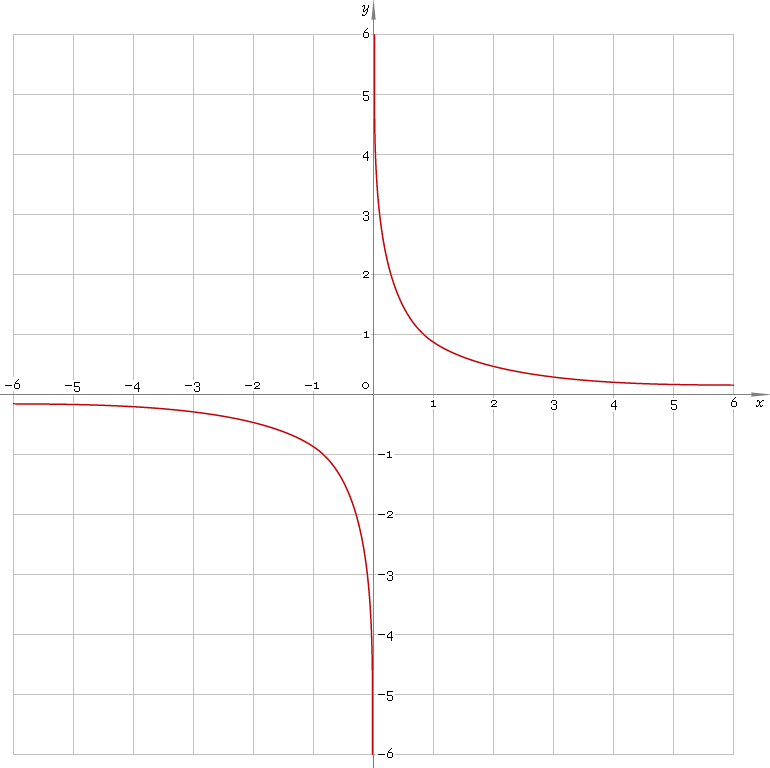 Fig. 1. Plot of the arc-hyperbolic cosecant function y = arcschx.
Fig. 1. Plot of the arc-hyperbolic cosecant function y = arcschx.
Function codomain is entire real axis, except 0: (−∞, 0)∪(0, +∞).
3. Identities
Property of antisymmetry:
arcsch−x = −arcschxReciprocal argument:
arcsch(1/x) = arsinhxSum and difference:
arcschx + arcschy = arcsch{xy / [x√(1 + 1 /x2) + y√(1 + 1 /y2)]}arcschx − arcschy = arcsch{xy / [y√(1 + 1 /y2) − x√(1 + 1 /x2)]}
4. Support
Arc-hyperbolic cosecant function arcsch of the real argument is supported by free version of the Librow calculator.
Arc-hyperbolic cosecant function arcsch of the complex argument is supported by professional version of the Librow calculator.
5. How to use
To calculate arc-hyperbolic cosecant of the number:
arcsch(-1);To calculate arc-hyperbolic cosecant of the current result:
arcsch(rslt);To calculate arc-hyperbolic cosecant of the number x in memory:
arcsch(mem[x]);
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||